Pricing strategies are the main profit drivers in eCommerce. As price is the key detail consumers compare in eCommerce, pricing strategies should be your number one focus area. Building winning pricing strategies is easy: find out how your customer value is delivered and ensure your pricing is part of it. In this article we introduce five best pricing strategy examples that are simple to follow and implement.
Increase Profits and Revenue using our Strategy Tool
Ecommerce Pricing Strategy checklist
-
101 actionable strategy tips
-
Simple impact assessment
-
Automatic dashboard on resolved issues
Ecommerce Pricing Strategy Checklist

Does your pricing strategy deliver customer value?
Are your customers in search of low prices or a premium service and experience? Customer value is the core of your pricing and you should integrate your pricing strategy into your marketing strategy.
Let us assume you are an eCommerce company. You have decided your position in the market, you are clear on customer value and how your pricing delivers it. Now you must consider some tactics to make your prices and strategy work. You can consider aspects like competitor actions, market conditions, consumer trends, and other variables, including product costs, to account for the pricing model of your goods. It is vital and something we have seen multiple times: sticking to a simple pricing strategy works best if it delivers the value the customer wants. You can easily win your competitors over by creating a simple, understandable pricing plan that includes customer value at the core.
As a retailer or an e-commerce player, you must decide right pricing strategies before advertising products to customers. In the list below, we will review five most common pricing approaches. You need to determine the best pricing strategy for your business.
Need Expert Guidance on Your Pricing Strategy?
Explore our pricing solutions to enhance your eCommerce strategy.
1. Competition-based pricing strategy
Competition-based pricing utilizes pricing data of competitors for similar products to set a base price for their products. Rather than focusing on production costs or the item’s value for the customer, this pricing method relies heavily on market data.
Think of it in this way. You have five competitors who sell the same product as you, and you categorize the products from the most high-end brand to the affordable brands. Then, you decide where you fit in.
What is the ideal situation for using competition-based pricing?
The reason companies rely on competition-based pricing or market pricing is simple. Market-based pricing strategy is an easy strategy, and you have complete control over your market position. In addition, market information gathered on competitors can give more insights than just pricing, which you can implement in your brand to replicate similar results.
The disadvantages are that it is hard for companies to sustain only competitive pricing if they are not actively adding value to customer experience and are lacking quality products. Also, one of the major pitfalls is that selling based on a competitor’s pricing can undermine your product and cost you revenue.
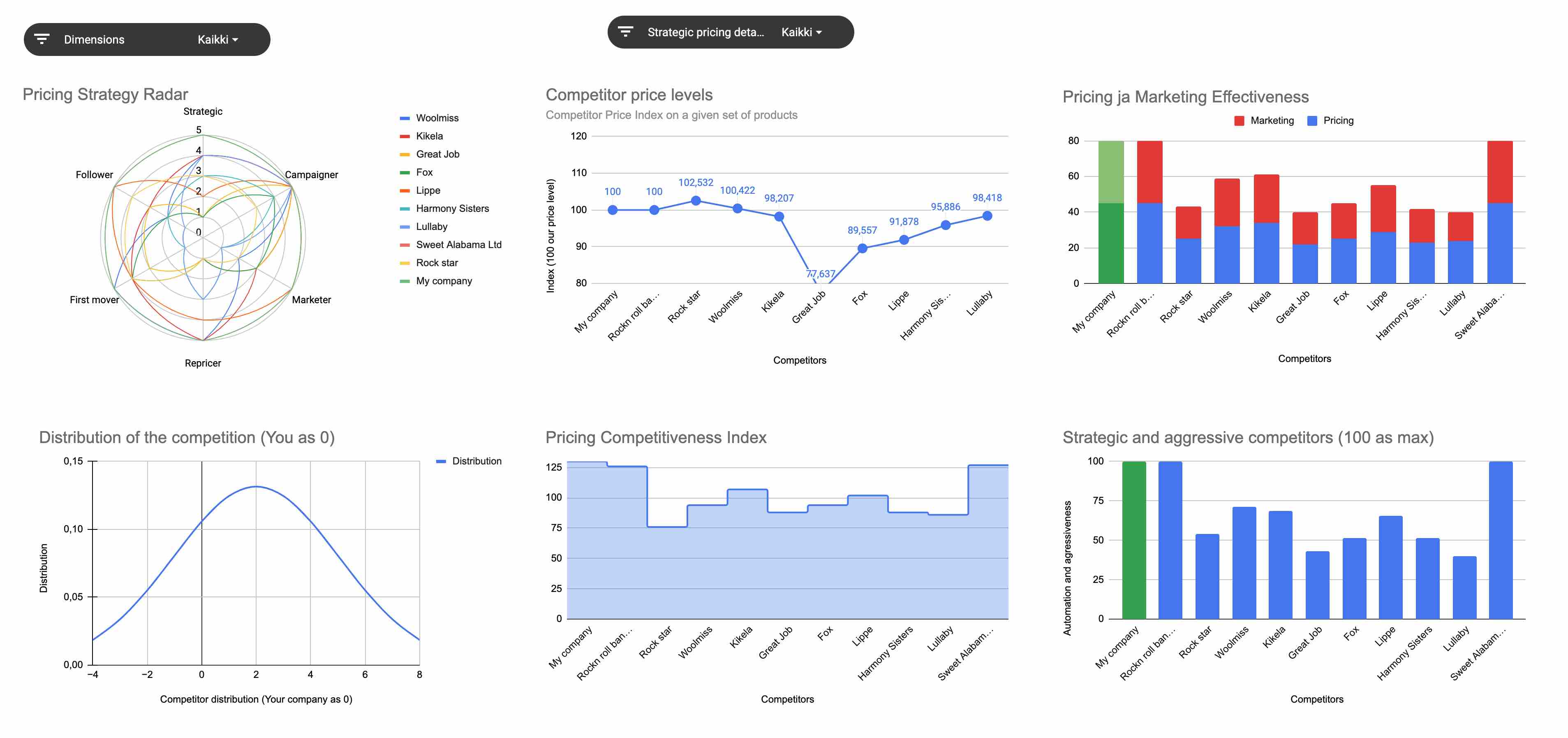
Analyse competitor pricing strategies
Insert information about your competitors to get clear dashboards and a comprehensive analysis of your competitors.
2. Cost-plus pricing strategy
Cost-plus pricing strategy or cost-based pricing strategy is an essential strategy that takes into account the total cost of making a product and adds a markup to that to determine the real price of a product. Although it is a good and straightforward strategy, as a business owner, you must understand the costs involved in production: material, labor, warehousing, machinery, utilities and such. The markup price added to the top of production cost is what the company makes in profit.
Here’s how cost-plus pricing works:
- Step 1: calculate the entire production cost for x units of a product.
- Step 2: divide the cost by x units to get the unit cost.
- Step 3: multiply unit cost by markup percentage. If unit cost is $10 and markup percentage is 20, then the profit margin is $10 X 20/100 = $2. The price of the product is $12.
Based on the products that are offered, they can charge different markups. However, this is not ideal for example software service companies and music producers as the product price is significantly higher than the product cost.
Understand your pricing
Get valuable insights on how different discounting techniques, costs and marketing will affect your profitability.

3. Dynamic pricing strategy
The simplest way to describe dynamic pricing is that your prices are not static but they change based on other factors. These factors can be, for example, segments, time, market changes or competitor prices. In eCommerce, the use of dynamic pricing in market-based pricing strategies is very common.
Dynamic pricing in different segments
Companies use algorithms and Dynamic Pricing Software to derive their prices for different groups based on statistics. Let’s look at an example. You own a car rental company and use AI-algorithms for pricing. You designed those to raise prices at locations with many pubs and bars. If this sounds highly illegal and impractical, we can assure you it is not. We are just describing Uber. Dynamic pricing, also known as adaptive pricing, is standard practice to raise profitability.
Dynamic pricing by time
Sales-based companies, like a car or insurance dealerships, are in a rush to close deals at the end of the month. As a result, dealers offer lower prices on products to match the sales quota compared to the start of the month. In today’s world, we see this happen all the time. For example, Amazon, Uber, and aviation companies use dynamic marketing based on supply and demand.
Read our latest post on dynamic pricing
Read “How to use competitor pricing to improve your profitability” and use our 15-step guide to get started and better understand your competition.
4. Penetration price strategy
Penetration pricing is used to capture market share by setting product prices at a below-market level to gain customers. Once you get a sizeable market share, you readjust your pricing accordingly.
Here’s how penetration pricing works
Let’s look at an example of penetration pricing. Consider company X, a small to a medium-sized soap maker, that sells lavender soap bars at $10. An international company Y, with a higher production capacity, enters the market and begins to sell a similar lavender soap bar at $5.
The goal of Y is to run the small-sized competitor X out of business even if at $5 company Y makes a low minimal profit. Still company Y is confident that company X cannot match their prices. As customers begin to buy from Y, X will eventually run out of business. This extreme form of penetrative pricing is also often called predatory pricing. World-renowned Walmart is known for relying on this practice and has been the bane of smaller local businesses due to their unmatchable price.
Learn how to build pricing strategies
With the help of our article on an introduction to pricing strategies, easily fine-tune or build your pricing strategy from scratch.
5. Price skimming strategy
The practice of charging a higher price point for a product when launching it is known as price skimming. Instead of this, you can leverage market demand and then lower or readjust the price based on price elasticity later.
We see this often at the launch of celebrity product lines or new product launches from a reputed brand. In these cases, customers are willing to pay considerably higher prices. Whether the price reflects the actual value of the product is not essential. Customers want the anticipated product, whether it is Rihanna’s Fenty Beauty or the newest Playstation, when the demand is high.
Lowering the price of products attracts price-sensitive customers. Therefore, you can charge the maximum amount for each customer segment by skimming off the top of these customer segments and get higher profits as a business owner. Monitor if you need to lower the price in a few months.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Businesses can effectively combine multiple pricing strategies by carefully analyzing their target market, competition, and product offerings. For example, they may use cost-plus pricing to ensure profitability while incorporating dynamic pricing to adjust prices based on market conditions and customer demand. By understanding customer value and market dynamics, companies can tailor their pricing strategies to maximize profits while remaining competitive.
Ethical considerations and potential drawbacks associated with certain pricing strategies should indeed be carefully evaluated by businesses. While penetration pricing can help capture market share, predatory pricing practices can harm competition and lead to antitrust issues. You should ensure that your pricing strategies comply with legal regulations to avoid negative consequences and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders.
One tip we have is you should make sure your master data is formalized and as well completed as possible. Additionally, with software you can conduct thorough testing and analysis to optimize pricing strategies and ensure accurate and efficient price adjustments that align with your business objectives and customer expectations.



